How are Galaxies formed?
There are two types of galaxies: Elliptical and spiral
Spiral galaxies are formed from the collapse of a protogalactic cloud. It consists of three components known as a rotating disk, bulge and halo. As the protogalactic cloud collapses then firstly, the stars in the bulge and halo are formed. The stars formed due to collapse have somewhat random orbits with the galactic centre and the remainder of the cloud forms a disk due to the conservation of angular momentum (angular momentum conservation can be seen in the effect when the spinning up of the artist pulls her arms inside to rotate faster). The formation of stars in the disk occurs shortly and hence the populations of stars in disk are younger than that of the bulge and the halo. Moreover unlike the stars in the bulge and halo, the stars in the disk revolve around the centre of the galaxy in a collective way as well as in defined way.
Elliptical galaxies are considered to be formed due to the merging of two disk galaxies. If two spiral galaxies merge together then the orbits of all the stars gets randomised. Consequently, all the stars in an elliptical galaxy have random orbits and the motions of stars are not in collective or defined way.
Spiral galaxies are formed from the collapse of a protogalactic cloud. It consists of three components known as a rotating disk, bulge and halo. As the protogalactic cloud collapses then firstly, the stars in the bulge and halo are formed. The stars formed due to collapse have somewhat random orbits with the galactic centre and the remainder of the cloud forms a disk due to the conservation of angular momentum (angular momentum conservation can be seen in the effect when the spinning up of the artist pulls her arms inside to rotate faster). The formation of stars in the disk occurs shortly and hence the populations of stars in disk are younger than that of the bulge and the halo. Moreover unlike the stars in the bulge and halo, the stars in the disk revolve around the centre of the galaxy in a collective way as well as in defined way.
Elliptical galaxies are considered to be formed due to the merging of two disk galaxies. If two spiral galaxies merge together then the orbits of all the stars gets randomised. Consequently, all the stars in an elliptical galaxy have random orbits and the motions of stars are not in collective or defined way.


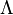 Cold Dark Matter cosmology; that is to say that clustering and merging is how galaxies gain in mass, and can also determine their shape and structure.
Cold Dark Matter cosmology; that is to say that clustering and merging is how galaxies gain in mass, and can also determine their shape and structure.