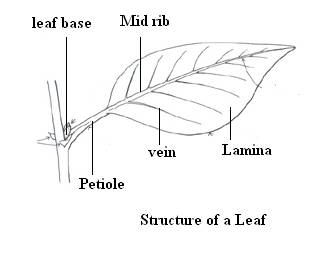
Internal Features
The leaf blade is composed of several layers as follows: [Figure 1]
· Epidermis – Outer layer of tissues
· Cuticle – Waxy protective outer layer of epidermis that prevents water loss on leaves, green stems, and fruits. The amount of cutin or wax increases with light intensity.
· Leaf hairs – part of the epidermis
· Palisade layer – A tightly packed layer of parenchyma tissues filled with chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
· Chloroplasts – Sub-cellular, photosynthetic structures in leaves and other green tissues. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a green plant pigment that captures the energy in light and begins the transformation of that energy into sugars.
· Vascular bundle – Xylem and phloem tissues, commonly known as leaf veins.
· Spongy mesophyll – Layer of parenchyma tissues loosely arranged to facilitate movement of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. It also may contain some chloroplasts.
· Stomata – Natural openings in leaves and herbaceous stems that allow for gas exchange (water vapor, carbon dioxide, and oxygen).
· Guard cells – Specialized kidney-shaped cells that open and close the stomata.

Figure 1. Leaf cross section with stomata.HOPE THIS HELPS !!!
THUMSB UP PLEASE