take a transversal , name it t and line l and m two angles in side the transversal but not in the sam side of the transversal
- 1
Alternate Interior Angles Definition
The angles which are formed inside the two parallel lines, when intersected by a transversal, are equal to their alternate pairs. These angles are called alternate interior angles.

In the above-given figure, you can see, two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal. Therefore, the alternate angles inside the parallel lines will be equal.
Properties
- These angles are congruent.
- The sum of the angles formed on the same side of the transversal which are inside the two parallel lines is always equal to 180°.
- In the case of non – parallel lines, alternate interior angles don’t have any specific properties.
Theorem and Proof
Statement: The theorem states that “ if a transversal crosses the set of parallel lines, the alternate interior angles are congruent”.
Given: a//d
To prove: ∠4 = ∠5 and ∠3 = ∠6
Proof: Suppose a and d are two parallel lines and l is the transversal that intersects a and d at points P and Q. See the figure.
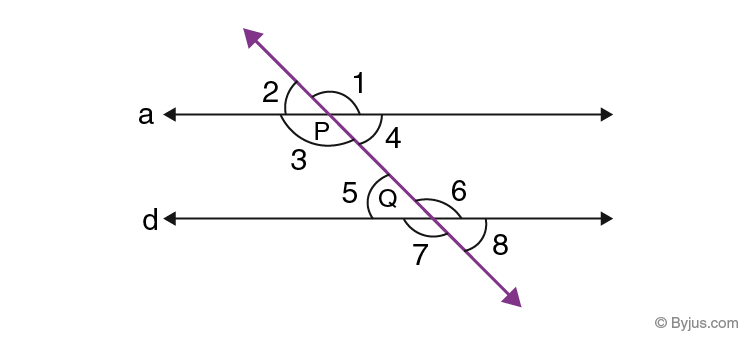
From the properties of the parallel line, we know if a transversal cuts any two parallel lines, the corresponding angles and vertically opposite angles are equal to each other. Therefore,
∠2 = ∠5 ………..(i) [Corresponding angles]
∠2 = ∠4 ………..(ii) [Vertically opposite angles]
From eq. (i) and (ii), we get;
∠4 = ∠5 [Alternate interior angles]
Similarly,
∠3 = ∠6
Antithesis of Theorem
If the alternate interior angles produced by the transversal line on two coplanar are congruent, then the two lines are parallel to each other.
Given: ∠4 = ∠5 and ∠3 = ∠6
To prove: a//b
Proof: Since ∠2 = ∠4 [Vertically opposite angles]
So, we can write,
∠2 = ∠5, which are corresponding angles.
Therefore, a is parallel to b.
Co-interior Angles
Co-interior angles are the two angles that are on the same side of the transversal. Co-interior angles are the interior angles and it sums up to 180 degrees. It means that the sum of two interior angles, which are on the same side of transversal is supplementary. Co-interior angles resemble like in “C” shape and both the angles are not equal to each other. The co-interior angle is also known as the consecutive interior angles or the same side interior angles.
Co-interior Angle Theorem and Proof
If the transversal intersects the two parallel lines, each pair of co-interior angles sums up to 180 degrees (supplementary angles).
Proof:

Let us consider the image given above:
In the figure, angles 3 and 5 are the co interior angles, and angles 4 and 6 are the co-interior angles.
To prove: ∠3 and ∠5 are supplementary and ∠4 and ∠6 are supplementary.
Given that, a and b are parallel to each other and t is the transversal.
By the definition of linear pair,
∠1 and ∠3 forms the linear pair.
Similarly, ∠2 and ∠4 form the linear pair.
By using the supplement postulate,
∠1 and ∠3 are supplementary
(i.e.) ∠1 + ∠3 = 180
Similarly,
∠2 and ∠4 are supplementary
(i.e.) ∠2 + ∠4 = 180
By using the corresponding angles theorem, we can write
∠1 ≅∠5 and ∠2 ≅ ∠6
Thus, by using the substitution property, we can say,
∠3 and ∠5 are supplementary and ∠4 and ∠6 are supplementary.
Hence, the co-interior angle theorem (consecutive interior angle) is proved.
The converse of this theorem is “if a transversal intersects two lines, such that the pair of co-interior angles are supplementary, then the two lines are parallel”.
Examples
Question 1:
Find the value of B and D in the given figure.
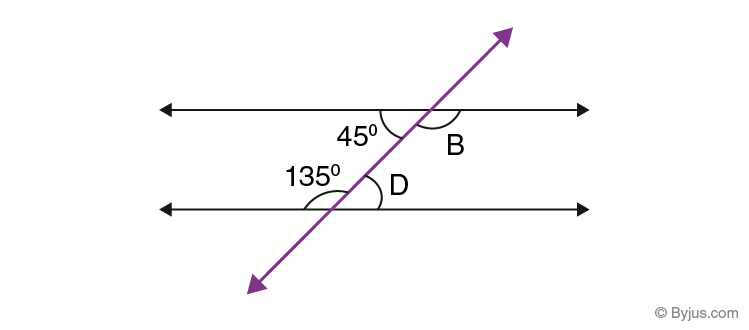
Solution:
Since 45° and D are alternate interior angles, they are congruent.
So, D = 45°
Since 135° and B are alternate interior angles, they are congruent.
So, B = 135°
Question 2:
Find the missing angles A, C, and D in the following figure.
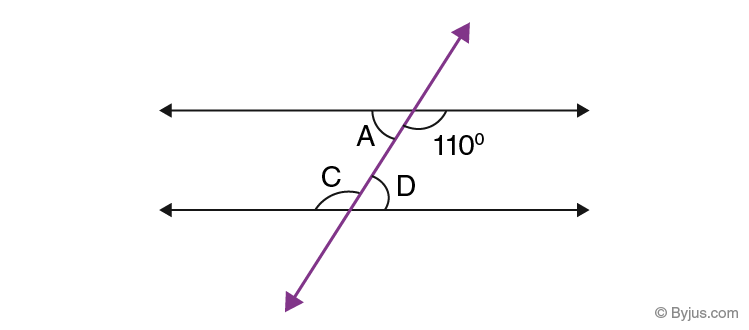
Solution:
As angles ∠A, 110°, ∠C and ∠D are all alternate interior angles, therefore;
∠C = 110°
By supplementary angles theorem, we know;
∠C+∠D = 180°
∠D = 180° – ∠C = 180° – 110° = 70°
Example 3:
Find the value of x from the given below figure.

Solution:
We know that alternate interior angles are congruent.
Therefore, 4x – 19 = 3x + 16
4x – 3x = 19+16
x = 35
Since,
∠A = ∠D
Therefore, ∠A = 70°.
- 0


