what is the difference between fossa ovalis and foramen ovale?plz explain diagrametically..
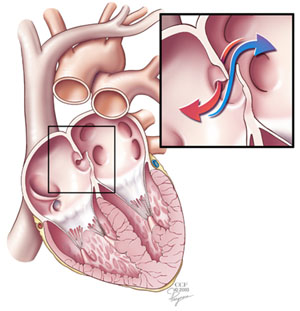
The fossa ovalis is a depression in the right atrium of the heart, at the level of the interatrial septum, the wall between right and left atrium. The fossa ovalis is the remnant of a thin fibrous sheet that covered the foramen ovale during fetal development.
Function
During fetal development, the foramen ovale allows blood to pass from the right atrium to the left atrium, bypassing the nonfunctional fetal lungs while the fetus obtains its oxygen from the placenta. A flap of tissue called the septum primum acts as a valve over the foramen ovale during that time. After birth, the introduction of air into the lungs causes the pressure in the pulmonary circulatory system to drop. This change in pressure pushes the septum primum against the atrial septum, closing the foramen. The septum primum and atrial septum eventually fuse together to form a complete seal, leaving a depression called the fossa ovalis. By age two, about 75% of people have a completely sealed fossa ovalis. An unfused fossa ovalis is called a patent foramen ovale. Depending on the circumstances, a patent foramen ovale may be completely asymptomatic, or may require surgery.The limbus of fossa ovalis (annulus ovalis) is the prominent oval margin of the fossa ovalis in the right atrium. It is most distinct above and at the sides of the fossa ovalis; below, it is deficient. A small slit-like valvular opening is occasionally found, at the upper margin of the fossa, leading upward beneath the limbus, into the left atrium; it is the remains of the fetal aperture the foramen ovale between the two atria.
Clinical significanceTricuspid valve stenosis
When the foramen does not close, blood can travel between the left and right atria, mixing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. The foramen ovale usually shuts by age one. Several problems can occur if the hole is left open. The right atrium may develop higher than normal pressure, which interferes with the blood's passage through the tricuspid valve, resulting in tricuspid valve stenosis. Tricuspid valve stenosis does not usually require treatment, though if the heart valves begin to malfunction, surgery may be needed.
Aneurysms can occur in adulthood if the foramen ovale is not closed correctly. An aneurysm happens when an artery becomes enlarged in a localized area due to weakening of the arterial wall.
When this type of aneurysm occurs in the area of the fossa ovalis, an enlarged pouch is formed. This pouch can protrude into the right atrium or the left atrium. The cause of this aneurysm is the result of abnormal, increased pressure within the heart. Even if the foramen ovale does seal shut, an aneurysm may occur, usually on the side of the right atrium. If the aneurysm stretches too far, it can narrow the opening of the inferior vena cava.This type of aneurysm can be a result of plaque build-up in the arteries from coronary heart disease, as well as diseases of the aortic valve or mitral valve. Surgery may be useful in helping to cope with the aneurysm.
If the atrial septum does not close properly, it leads to a patent foramen ovale (PFO). This type of defect generally works like a flap valve, opening during certain conditions of increased pressure in the chest, such as during strain while having a bowel movement, cough, or sneeze. With enough pressure, blood may travel from the right atrium to the left. If there is a clot in the right side of the heart, it can cross the PFO, enter the left atrium, and travel out of the heart and to the brain, causing a stroke. If the clot travels into a coronary artery it can cause a heart attacK


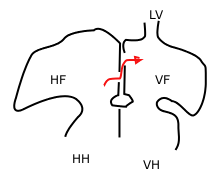 Sketch showing foramen ovale in a fetal heart. Red arrow shows blood from the inferior cava traveling to the right atrium and then to the left atrium. HF: right atrium, VF: left atrium. HH and VH: right and left ventricle. The heart still has a common pulmonary vein (LV), instead of four.
Sketch showing foramen ovale in a fetal heart. Red arrow shows blood from the inferior cava traveling to the right atrium and then to the left atrium. HF: right atrium, VF: left atrium. HH and VH: right and left ventricle. The heart still has a common pulmonary vein (LV), instead of four.
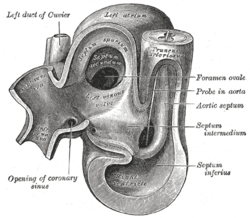 Heart of human embryo of about thirty-five days, opened on left side.
Heart of human embryo of about thirty-five days, opened on left side.