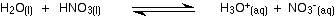Negative deviations from Raoult's Law
In exactly the same way, you can have mixtures with vapour pressures which are less than would be expected by Raoult's Law. In some cases, the deviations are small, but in others they are much greater giving a minimum value for vapour pressure lower than that of either pure component.
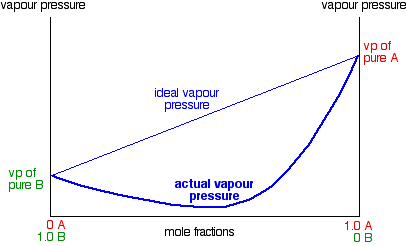
Explaining the deviations
These are cases where the molecules break away from the mixture less easily than they do from the pure liquids. New stronger forces must exist in the mixture than in the original liquids.
You can recognise this happening because heat is evolved when you mix the liquids - more heat is given out when the new stronger bonds are made than was used in breaking the original weaker ones.
Many (although not all) examples of this involve actual reaction between the two liquids. The example of a major negative deviation that we are going to look at is a mixture of nitric acid and water. These two covalent molecules react to give hydroxonium ions and nitrate ions.

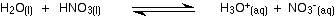
You now have strong ionic attractions involved.
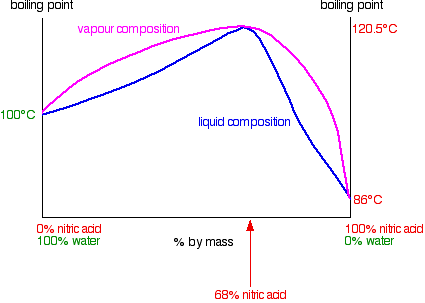
A large negative deviation from Raoult's Law: nitric acid and water mixtures
Nitric acid and water form mixtures in which particles break away to form the vapour with much more difficulty than in either of the pure liquids. You can see this from the vapour pressure / composition curve discussed further up the page.
That means that mixtures of nitric acid and water can have boiling points higher than either of the pure liquids because it needs extra heat to break the stronger attractions in the mixture.
In the case of mixtures of nitric acid and water, there is a maximum boiling point of 120.5C when the mixture contains 68% by mass of nitric acid. That compares with the boiling point of pure nitric acid at 86C, and water at 100C.
Notice the much bigger difference this time due to the presence of the new ionic interactions (see above).
The phase diagram looks like this: